In the ever-evolving digital landscape, navigating the complexities of data privacy regulations has become a paramount concern for businesses worldwide. 2024 promises to be a year of significant change, with new laws being implemented and existing ones being amended, creating a dynamic and intricate regulatory environment. From the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe to the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, organizations must adapt to the evolving landscape of data protection, ensuring compliance and safeguarding sensitive information.
This article delves into the key trends shaping data privacy regulations in 2024, exploring the latest developments, emerging challenges, and best practices for organizations to navigate this complex terrain. We will analyze the impact of key legislation like the GDPR and CCPA, discuss the rise of new regulations, and provide insights into the future of data privacy. Whether you’re a seasoned data privacy professional or just starting to grapple with these issues, this comprehensive guide offers valuable information to empower you in building a robust and compliant data protection strategy for your organization.
Key Data Privacy Regulations Impacting Businesses in 2024
As we enter 2024, businesses are navigating a complex and rapidly evolving landscape of data privacy regulations. These regulations are designed to protect individuals’ personal data, and non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage. Here are some key data privacy regulations that businesses need to be aware of in 2024:
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR, which came into effect in 2018, continues to be a cornerstone of data privacy legislation in Europe. It applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU residents, regardless of where the organization is located. Key requirements of the GDPR include:
- Transparency: Clear and concise information about data processing activities.
- Purpose limitation: Data can only be collected and processed for specified, legitimate purposes.
- Data minimization: Only necessary data should be collected and processed.
- Data subject rights: Individuals have the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict, and object to their data processing.
- Data security: Organizations must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA, which went into effect in 2020, is a significant data privacy law in California. It provides California residents with specific rights regarding their personal data, including the right to know, the right to access, the right to delete, and the right to opt-out of the sale of their data.
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)
The VCDPA, which went into effect in 2023, is another important state-level data privacy law in the US. It provides similar protections to the CCPA, requiring organizations to inform consumers about the personal data they collect, provide access to that data, and allow consumers to request deletion.
The Brazil General Data Protection Law (LGPD)
The LGPD, which went into effect in 2020, is a comprehensive data protection law in Brazil. It applies to any organization that processes the personal data of Brazilian residents, regardless of where the organization is located. The LGPD requires organizations to implement appropriate security measures, obtain consent before processing personal data, and provide individuals with access to their data.
The Canadian Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
PIPEDA, which went into effect in 2000, is a federal privacy law in Canada. It applies to organizations that collect, use, or disclose personal information in the course of commercial activities. Key requirements of PIPEDA include obtaining consent for data collection, limiting collection to what is necessary, and ensuring the security of personal data.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
Staying up-to-date on data privacy regulations is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Organizations should:
- Conduct regular audits: To identify and address any potential compliance gaps.
- Implement strong data security measures: To protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- Train employees: On data privacy best practices.
- Consult with legal experts: To ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
By taking these steps, businesses can ensure they are protecting personal data and avoiding potential legal and reputational risks in 2024 and beyond.
GDPR: Updates and Enforcement Trends
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has become a cornerstone of data privacy regulations globally, shaping how organizations handle personal data. As we step into 2024, the landscape of data privacy continues to evolve, with notable updates and enforcement trends influencing how businesses need to navigate this complex regulatory environment.
One of the key developments in 2024 is the increased focus on data subject rights. The GDPR grants individuals extensive rights regarding their personal data, including the right to access, rectify, erase, and restrict processing. Regulators are emphasizing the importance of organizations upholding these rights effectively and transparently, prompting a shift towards more robust data subject request management processes.
Enforcement actions have also intensified, with the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) taking a more proactive approach. Organizations are facing greater scrutiny from data protection authorities (DPAs) regarding their compliance practices, including data breach notification procedures, data transfer mechanisms, and data security measures. Significant fines have been levied on companies that fail to comply with GDPR regulations, highlighting the substantial financial risks associated with non-compliance.
The GDPR is also becoming increasingly intertwined with other data privacy regulations, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Brazil General Data Protection Law (LGPD). This trend necessitates a holistic approach to data privacy compliance, considering the overlapping requirements and implications of various jurisdictions.
In conclusion, the GDPR’s impact on data privacy practices continues to evolve in 2024. With a heightened focus on data subject rights, increased enforcement actions, and the growing interconnectedness with other regulations, organizations need to remain vigilant in their compliance efforts. Adapting to these updates and trends is essential for ensuring responsible data handling and minimizing the risks associated with data privacy violations.
CCPA/CPRA: California’s Strict Data Privacy Regime
California has taken a leading role in data privacy with the passage of the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in 2018 and its subsequent amendment, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), which went into effect in January 2023. These laws have established a robust framework for consumer data privacy, significantly impacting businesses that operate in California or collect data from California residents. The CCPA/CPRA grants consumers extensive rights over their personal information, including the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their data.
The CPRA strengthens and expands upon the CCPA, bringing several significant changes:
- Enhanced consumer rights: The CPRA introduces new rights, such as the right to correct inaccurate data and the right to limit the use of sensitive personal information.
- Expanded scope of personal information: The CPRA broadens the definition of personal information, covering a wider range of data types.
- Greater enforcement authority: The CPRA creates a new California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) with increased enforcement powers, including the ability to impose significant fines.
- Increased obligations for businesses: The CPRA imposes new obligations on businesses, including the need to conduct privacy impact assessments and implement robust data security measures.
The CCPA/CPRA has far-reaching implications for businesses, requiring them to:
- Update privacy policies and procedures: To comply with the CCPA/CPRA, businesses must update their privacy policies and procedures to reflect the new requirements, including providing consumers with clear and concise information about their data practices.
- Implement data subject access requests (DSARs): Businesses must be prepared to handle DSARs from consumers, enabling them to access, delete, or opt out of the sale of their data.
- Adopt data security measures: The CCPA/CPRA mandates that businesses implement appropriate technical and organizational security measures to protect personal information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Develop a comprehensive privacy program: To comply with the CCPA/CPRA, businesses should develop a comprehensive privacy program that includes policies, procedures, and training for employees.
Navigating the complexities of the CCPA/CPRA requires businesses to remain informed about the evolving regulatory landscape and to proactively adapt their practices to ensure compliance. Businesses that fail to comply with the CCPA/CPRA face significant penalties, including fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
Emerging Global Privacy Laws: A Look at Key Jurisdictions
The landscape of data privacy regulations is constantly evolving, with new laws and updates emerging around the globe. As businesses operate in an increasingly interconnected world, navigating these complex regulations is crucial for protecting sensitive data and avoiding potential legal risks. This article provides an overview of key jurisdictions with emerging global privacy laws, highlighting the critical considerations for businesses operating in these regions.
The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of data privacy with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This comprehensive law, effective since 2018, sets strict standards for data processing, including consent requirements, data subject rights, and data breach notification obligations. The GDPR applies to any organization processing personal data of individuals located within the EU, regardless of the organization’s location.
Brazil has implemented the Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD), inspired by the GDPR, which came into effect in 2020. The LGPD provides comprehensive data protection measures, including the right to access, rectification, and erasure of personal data, as well as the obligation to obtain informed consent for data processing. The LGPD applies to any organization, regardless of its location, that processes personal data of individuals residing in Brazil.
California, USA, has adopted the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA). The CCPA, effective in 2020, provides consumers with specific rights regarding their personal information, including the right to know, access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their data. The CPRA, which will come into effect in 2023, builds upon the CCPA and establishes a new privacy agency to enforce data protection regulations.
China has implemented the Cybersecurity Law and the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), which became effective in 2020 and 2021, respectively. The Cybersecurity Law focuses on data security and protection, while the PIPL provides comprehensive data privacy regulations. The PIPL applies to organizations that process personal information of individuals located within China, regardless of the organization’s location.
India has enacted the Personal Data Protection Bill (PDPB), which is currently under review. The PDPB aims to establish a comprehensive data protection framework, covering areas such as consent, data processing, and data transfers. If enacted, the PDPB would significantly impact businesses operating in India.
As global data privacy regulations continue to evolve, it is essential for businesses to stay informed and adapt their practices accordingly. Understanding the key jurisdictions and their specific requirements can help organizations avoid legal risks, enhance their data protection strategies, and build trust with their customers.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: Best Practices
As data privacy regulations continue to evolve in 2024, organizations must prioritize data minimization and purpose limitation to ensure compliance and build trust with their customers. These principles are fundamental to responsible data handling, focusing on collecting and using only the necessary data for specific, legitimate purposes.
Data Minimization involves collecting only the data that is absolutely essential for a specific purpose. This means avoiding unnecessary information collection and focusing on obtaining only the data that is directly relevant to the intended use.
Purpose Limitation means clearly defining the purpose for which data is collected and ensuring that it is not used for any other purpose without explicit consent. This principle helps prevent the misuse of data and maintains transparency with individuals.
Best Practices for Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
- Conduct Data Audits: Regularly review the data you collect, identify unnecessary data points, and eliminate them from your systems.
- Implement Clear Data Collection Policies: Clearly communicate to your users why you need certain data and what you will use it for.
- Use Data Minimization Techniques: Utilize techniques like data masking, tokenization, and encryption to protect sensitive data.
- Obtain Explicit Consent: Get clear and informed consent from users before collecting their data for any purpose.
- Review Data Retention Policies: Establish and enforce data retention policies to delete or anonymize data that is no longer needed for its intended purpose.
- Promote Data Transparency: Be open and transparent about your data practices with your users. Provide them with easy-to-understand information about how you collect, use, and store their data.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can effectively embrace data minimization and purpose limitation, ensuring responsible and ethical data handling in the ever-evolving data privacy landscape.
Data Subject Rights: Access, Correction, and Deletion
As data privacy regulations continue to evolve in 2024, understanding data subject rights is paramount for both individuals and organizations. These rights empower individuals to control their personal information and ensure its responsible handling. Among the most fundamental rights are the rights to access, correct, and delete personal data.
The right to access allows individuals to request confirmation of whether their personal data is being processed, as well as access to information regarding the purpose of processing, the categories of data being processed, and the recipients of the data. This right empowers individuals to understand how their data is being used and to ensure its lawful processing.
The right to correction enables individuals to rectify inaccurate or incomplete personal data. This right ensures the accuracy and reliability of personal information, protecting individuals from potential harm caused by outdated or incorrect data.
Finally, the right to deletion, also known as the “right to be forgotten,” allows individuals to request the erasure of their personal data in certain circumstances. This right is particularly relevant when the data is no longer necessary for the original purpose of processing, or when it is being processed unlawfully.
Navigating the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations requires a clear understanding of data subject rights. Organizations must implement robust data management practices and establish transparent procedures for handling access, correction, and deletion requests. Individuals, in turn, should be aware of their rights and utilize them to ensure the responsible and ethical handling of their personal data.
Cross-Border Data Transfers: Ensuring Compliance
In today’s interconnected world, businesses frequently engage in cross-border data transfers, moving personal data across national boundaries. However, navigating the intricate landscape of data privacy regulations has become increasingly complex, with each jurisdiction imposing its own unique requirements. This article delves into the challenges and solutions surrounding cross-border data transfers in 2024, focusing on ensuring compliance with evolving data privacy regulations.
Key Regulatory Frameworks:
The most prominent data privacy regulations influencing cross-border data transfers include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Applicable in the European Economic Area (EEA), the GDPR sets stringent standards for processing personal data, including requirements for lawful transfer mechanisms.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): In the United States, California’s CCPA mandates specific data transfer provisions, particularly for businesses dealing with California residents’ data.
- Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD): The LGPD establishes comprehensive data protection principles and rules governing cross-border data transfers, requiring organizations to comply with specific requirements.
Challenges in Cross-Border Data Transfers:
Transferring personal data across borders presents various challenges, including:
- Conflicting Regulations: Each jurisdiction may have distinct data protection standards and requirements, making compliance a complex task for businesses operating globally.
- Data Localization Requirements: Some countries mandate that certain data types must be stored and processed within their borders, presenting obstacles for data transfer.
- Lack of Harmonization: The absence of consistent global data privacy regulations can create uncertainties and difficulties in ensuring compliance.
Ensuring Compliance:
Organizations need to adopt proactive measures to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations governing cross-border data transfers, including:
- Data Transfer Impact Assessments: Conducting comprehensive assessments to identify potential risks and compliance requirements for each data transfer.
- Appropriate Transfer Mechanisms: Implementing legally recognized transfer mechanisms, such as standard contractual clauses (SCCs), binding corporate rules (BCRs), or certification schemes, to ensure lawful data transfer.
- Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: Limiting data collection and processing to what is necessary for legitimate business purposes.
- Strong Security Measures: Implementing robust security controls to protect personal data during transfer and storage.
- Transparency and Accountability: Communicating clearly with individuals about data transfer practices and providing appropriate access and control over their data.
Conclusion:
In the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with cross-border data transfer requirements is paramount for organizations operating globally. By understanding the key regulatory frameworks, addressing the challenges, and adopting proactive compliance strategies, businesses can navigate this complex terrain and maintain data privacy integrity while fostering trust with their customers.
The Role of Consent and Transparency in Data Privacy
As we navigate the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations in 2024, the importance of consent and transparency in data handling cannot be overstated. These two pillars are fundamental to ensuring that individuals have control over their personal information and that organizations operate ethically and responsibly.
Consent is the cornerstone of data privacy. It signifies that individuals have been informed about how their data will be used and have freely agreed to its processing. This implies clear and concise language, avoiding technical jargon, and offering readily understandable explanations of data collection, processing, and retention practices.
Transparency complements consent. It involves providing individuals with comprehensive and readily accessible information about how their data is collected, used, shared, and secured. This means making data privacy policies readily available, providing clear and easily understandable explanations of data practices, and enabling individuals to access, correct, or delete their personal data.
By embracing consent and transparency, organizations can build trust with their users, demonstrate a commitment to ethical data handling, and mitigate potential risks associated with data breaches or misuse. In today’s data-driven world, these principles are not merely compliance requirements; they are essential elements for establishing a sustainable and responsible relationship with individuals and their data.
Data Security Measures: Protecting Sensitive Information
In the digital age, where data reigns supreme, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. As we navigate the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations in 2024, robust data security measures are not just a compliance requirement but a fundamental pillar of trust and ethical business practice.
At the core of data security lies a multi-layered approach. Encryption, the process of transforming data into an unreadable format, serves as a critical first line of defense. By encrypting data both at rest and in transit, organizations can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Access controls play a vital role in limiting who can view and modify sensitive data. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms and adhering to the principle of least privilege ensure that only authorized personnel have access to specific information.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential to identify and address potential weaknesses. Proactive measures, including penetration testing and continuous monitoring, help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, employee training is a crucial component of data security. Educating employees about best practices, such as secure password management and recognizing phishing attempts, significantly reduces the risk of human error.
In conclusion, implementing comprehensive data security measures is a continuous process that demands ongoing vigilance. By embracing encryption, access controls, regular audits, and employee training, organizations can create a secure environment for handling sensitive information in the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations.
Data Breach Response and Notification Requirements
In the ever-evolving landscape of data privacy regulations, staying ahead of the curve is paramount. One crucial aspect of compliance is understanding and implementing effective data breach response and notification requirements. These requirements vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the breach. However, the underlying principle remains the same: swift action to mitigate damage, protect affected individuals, and comply with legal obligations.
The core elements of a robust data breach response plan encompass:
- Incident Detection and Analysis: Early detection is critical. Establishing robust monitoring systems and proactive security measures can help identify breaches quickly.
- Containment and Mitigation: Once a breach is detected, prompt action is essential. Steps should be taken to contain the breach, prevent further data loss, and mitigate the impact on affected individuals.
- Notification Requirements: Different jurisdictions have specific timelines and notification protocols. Organizations must familiarize themselves with these requirements and promptly notify affected individuals, regulatory bodies, and relevant stakeholders.
- Data Recovery and Remediation: Organizations need to have a plan to recover compromised data and restore systems. This may include implementing data backups and recovery strategies, as well as conducting security audits and remediation efforts.
- Transparency and Communication: Open and transparent communication with affected individuals is crucial. Organizations should provide clear and concise information about the breach, the steps they are taking to mitigate the situation, and resources available to affected individuals.
Failure to comply with data breach notification requirements can result in substantial fines, reputational damage, and legal action. As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest requirements and implementing best practices for data breach response is crucial. Organizations must proactively prepare for potential data breaches, embrace a culture of data security, and prioritize the protection of personal information.
Penalties for Non-Compliance: The Cost of Ignoring Data Privacy
In 2024, the data privacy landscape is evolving rapidly, with new regulations being implemented and existing ones being enforced more rigorously. This means that businesses must be vigilant about their data privacy practices to avoid hefty fines and reputational damage. The potential penalties for non-compliance are a stark reminder that ignoring data privacy is not an option.
Financial penalties are a significant risk for businesses that fail to comply with data privacy regulations. These penalties can be substantial, ranging from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity of the violation and the jurisdiction. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) can impose fines of up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
Beyond financial penalties, businesses face a range of other risks, including:
- Reputational damage: Data breaches and privacy violations can severely damage a company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and confidence.
- Loss of business: Customers may choose to do business with competitors who have a stronger commitment to data privacy.
- Legal action: Individuals whose data has been mishandled can bring legal action against businesses, seeking compensation for damages.
- Competitive disadvantage: Companies that fail to comply with data privacy regulations may face difficulty doing business in certain jurisdictions.
The potential consequences of non-compliance are clear. Businesses must take data privacy seriously, implementing robust policies and procedures to protect sensitive information. This includes:
- Conducting regular data privacy audits
- Training employees on data privacy best practices
- Implementing strong data security measures
- Being transparent with customers about how their data is collected, used, and protected
By taking proactive steps to comply with data privacy regulations, businesses can mitigate their risks and build trust with customers. Ignoring data privacy is simply not an option in today’s digital world.
Preparing Your Organization for 2024’s Data Privacy Landscape

The data privacy landscape is constantly evolving, and 2024 promises to be no different. Organizations must stay ahead of the curve to avoid costly compliance failures and reputational damage. This means understanding the key trends shaping data privacy regulations and taking proactive steps to prepare.
Here are some of the key trends that will shape the data privacy landscape in 2024:
- Increased enforcement: Regulatory bodies are becoming increasingly aggressive in enforcing data privacy laws. This means organizations can expect to see more fines, audits, and investigations.
- Expansion of data privacy laws: New data privacy laws are being introduced in various regions. Organizations need to stay informed about these new regulations and ensure their data practices comply.
- Growing importance of data security: Data breaches continue to be a major concern. Organizations need to invest in robust data security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Focus on consumer rights: Consumers are becoming more aware of their data privacy rights and demanding greater control over their personal data. Organizations need to be transparent about their data practices and offer consumers clear choices about how their data is used.
- Emergence of new technologies: Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and other technologies are raising new data privacy challenges. Organizations need to consider the implications of these technologies and develop appropriate safeguards.
To prepare for these challenges, organizations need to take a comprehensive approach to data privacy. This includes:
- Conducting a data privacy risk assessment: Identify and assess the risks associated with your organization’s data handling practices.
- Implementing a data privacy program: Develop a comprehensive program that includes policies, procedures, and training to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Appointing a data privacy officer: Assign a dedicated individual to oversee data privacy compliance efforts.
- Building a culture of data privacy: Promote awareness and understanding of data privacy principles throughout the organization.
- Investing in technology: Leverage technology solutions to help manage data privacy compliance, such as data masking, encryption, and access control tools.
- Staying informed: Monitor developments in data privacy regulations and best practices.
By taking these steps, organizations can ensure they are prepared for the evolving data privacy landscape and avoid costly compliance failures. Remember, data privacy is not just a legal requirement; it is also essential for building trust with customers and protecting your organization’s reputation.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Data Privacy Trends to Watch
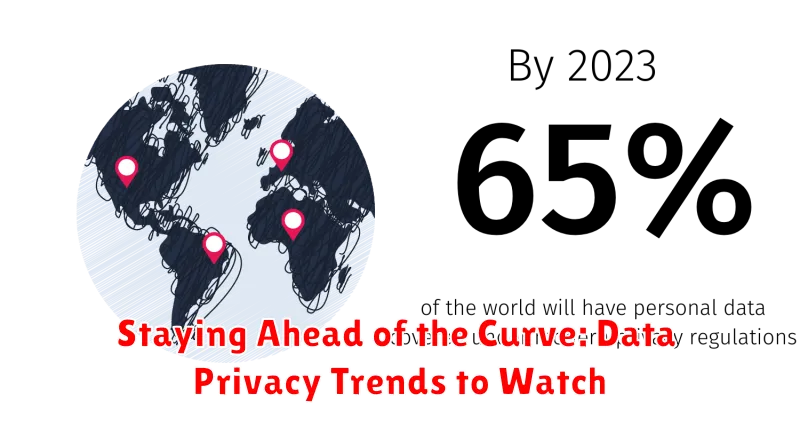
The landscape of data privacy regulations is constantly evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for businesses. As we move into 2024, it is crucial to stay informed about emerging trends to ensure compliance and maintain customer trust. Here are some key areas to watch:
1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Privacy: The increasing use of AI in data processing raises new privacy concerns. Regulations are beginning to address how AI systems collect, use, and store personal data. Businesses need to implement robust data governance frameworks and ensure transparency in their AI applications.
2. Expanding Scope of Data Protection: Many jurisdictions are broadening the definition of personal data, encompassing information like online identifiers and biometric data. Organizations must expand their data privacy practices to cover this wider range of information and ensure compliance with evolving definitions.
3. Cross-Border Data Transfers: Global data flows are becoming more complex, and regulations are increasingly strict on transferring data across borders. Businesses need to carefully assess their data transfer mechanisms and implement appropriate safeguards to ensure compliance with different regional laws.
4. Increased Focus on Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: Regulations are emphasizing the importance of collecting only necessary data and using it solely for the stated purpose. Organizations must adopt data minimization strategies and implement robust data retention policies.
5. Growing Importance of Data Subject Rights: Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of their data rights. Businesses need to provide clear and accessible information about data collection and processing practices. They must also ensure efficient mechanisms for exercising data subject rights, such as access, rectification, and erasure.
Staying ahead of these trends is essential for businesses operating in the digital age. By proactively implementing robust data privacy practices and staying informed about evolving regulations, organizations can navigate the evolving landscape of data privacy and maintain a competitive edge.

