The cloud has become an essential tool for businesses of all sizes, offering a range of benefits including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and increased agility. However, navigating the complexities of cloud migration can be daunting. With so many different cloud providers, services, and strategies available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the information and insights you need to successfully migrate your business to the cloud, leveraging proven strategies to ensure a smooth transition.
Whether you’re just starting to explore the cloud or are looking to optimize your existing cloud infrastructure, this guide will be your roadmap. We’ll cover everything from assessing your current environment and choosing the right cloud platform to developing a comprehensive migration plan and managing the transition process. By understanding the key considerations and best practices for cloud migration, you can maximize the benefits of the cloud and achieve your business objectives.
Understanding Cloud Migration: Why Move to the Cloud?
In today’s digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to the cloud to enhance their operations and gain a competitive edge. But why is cloud migration so popular? What are the key benefits that drive organizations to embrace this transformative journey?
The answer lies in the numerous advantages that cloud computing offers. Cost savings is a major driver, as cloud services eliminate the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure investments. This allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use, leading to significant cost reductions in the long run.
Scalability and flexibility are other key benefits. Cloud environments allow businesses to easily scale their resources up or down based on their needs. This means they can adapt quickly to changing demands and avoid costly overprovisioning or underprovisioning of resources. The cloud also offers a high degree of flexibility, enabling businesses to access and utilize resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
Furthermore, the cloud provides enhanced security. Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, offering robust protection against data breaches and cyberattacks. This can provide businesses with peace of mind and ensure the safety of their sensitive information. Improved performance and reliability are additional advantages. Cloud services leverage cutting-edge technologies and infrastructure, delivering superior performance and uptime compared to traditional on-premises solutions.
Finally, the cloud offers a wide range of innovative services that can help businesses streamline their operations and enhance their offerings. These services include big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights from their data, automate tasks, and improve their decision-making processes.
Types of Cloud Migration Strategies: Choosing the Right Approach
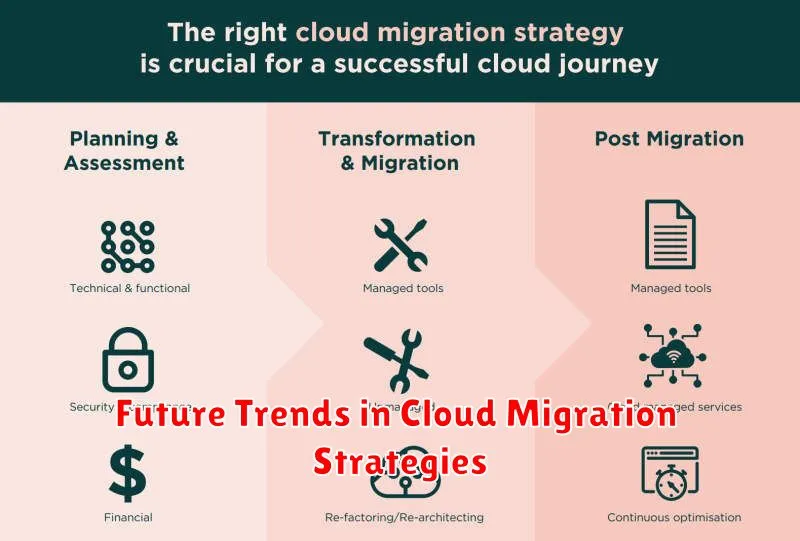
Migrating to the cloud is a major undertaking, and choosing the right strategy is crucial for a successful transition. There are several different cloud migration strategies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these strategies will help you select the best approach for your organization’s specific needs and goals.
Here are some common cloud migration strategies:
1. Big Bang Migration
This strategy involves migrating all your applications and data to the cloud in one go. It’s the fastest approach, but it also carries the highest risk. If something goes wrong, it can disrupt your entire business. This strategy is best suited for small organizations with simple applications and a low tolerance for downtime.
2. Phased Migration
A phased migration involves migrating your applications and data in stages. This approach is less risky than a big bang migration, but it can take longer to complete. This strategy is a good option for organizations with complex applications or a high tolerance for downtime.
3. Lift and Shift
This strategy involves migrating your applications and data to the cloud without making any changes to them. It’s the simplest and fastest approach, but it may not be the most efficient. Lift and shift is a good option for applications that are not heavily reliant on on-premises resources.
4. Re-platforming
This strategy involves migrating your applications to the cloud while making some changes to them to take advantage of cloud-native technologies. This approach can improve performance and efficiency, but it requires more effort than a lift and shift migration. Re-platforming is a good option for applications that are well-suited for the cloud but require some adjustments.
5. Replatforming
Replatforming involves completely re-architecting your applications to take full advantage of the cloud’s capabilities. This strategy can deliver the greatest benefits, but it also requires the most time and effort. Replatforming is a good option for applications that are not well-suited for the cloud and require a complete overhaul.
The best cloud migration strategy for your organization depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of your applications, your tolerance for downtime, and your budget. Carefully consider your options and choose the strategy that best aligns with your needs and goals.
Key Considerations for a Successful Cloud Migration
Embarking on a cloud migration journey can be both exciting and daunting. To ensure a smooth and successful transition, it’s crucial to carefully consider several key factors. This article will guide you through essential aspects that will contribute to a seamless and beneficial migration.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before diving into the technical aspects, it’s essential to establish your migration goals. What do you hope to achieve through this move? Increased agility, cost optimization, or improved scalability? Defining clear objectives will provide a roadmap and help you measure the success of your migration.
2. Choose the Right Cloud Provider
The cloud landscape is vast, offering diverse solutions from various providers. Research and select a provider that aligns with your specific needs, technical requirements, and budget. Consider factors like security, compliance, and service level agreements (SLAs) to make an informed decision.
3. Assess Your Existing Infrastructure
Thorough assessment is crucial. Carefully evaluate your on-premises infrastructure, including applications, data, and dependencies. Identify any potential compatibility issues or required modifications to ensure a smooth migration process.
4. Develop a Comprehensive Migration Strategy
A well-defined strategy is essential. Outline the migration phases, timelines, and responsibilities for each stage. Choose the appropriate migration method (lift and shift, re-platforming, or re-architecting) based on your application requirements and budget.
5. Prioritize Data Security and Compliance
Data security is paramount. Ensure that your chosen cloud provider offers robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations. Develop a data migration plan that prioritizes security and minimizes risks.
6. Plan for Testing and Rollback
Thorough testing is crucial to identify and resolve any potential issues before going live. Establish a comprehensive testing plan that includes functional, performance, and security tests. Also, ensure that you have a well-defined rollback strategy in case of unexpected problems.
7. Embrace Training and Support
Invest in training for your team to familiarize them with the new cloud environment. Ensure that you have access to adequate support from the cloud provider or trusted third-party vendors to address any technical challenges during and after the migration.
8. Monitor and Optimize
Post-migration monitoring is essential to track performance, resource utilization, and security. Continuously optimize your cloud environment for cost efficiency and performance improvement. Leverage cloud monitoring tools and analytics to gain insights and make informed adjustments.
By carefully considering these key considerations, you can pave the way for a successful cloud migration journey. Remember that each migration is unique, so tailor your approach to suit your specific needs and circumstances. With a well-defined plan, thorough preparation, and a commitment to continuous improvement, you can unlock the full potential of the cloud and achieve your desired business outcomes.
Planning Your Cloud Migration: A Step-by-Step Guide
Embarking on a cloud migration journey can be a transformative experience for your business, offering enhanced scalability, cost efficiency, and agility. However, a successful migration requires meticulous planning to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions. This step-by-step guide provides a comprehensive framework for navigating your cloud migration strategy.
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before diving into the technical aspects, clearly define your migration goals and objectives. Determine what you hope to achieve by moving to the cloud, such as:
- Increased scalability and flexibility
- Reduced operational costs
- Improved security and compliance
- Enhanced disaster recovery capabilities
2. Conduct a Thorough Assessment
A comprehensive assessment is crucial for identifying your current infrastructure’s strengths and weaknesses. Analyze your existing applications, data storage, network configurations, and security posture. This assessment will help you determine the best cloud platform and services for your needs.
3. Select the Right Cloud Platform
The cloud landscape is vast, with numerous platforms available, each with its own strengths and limitations. Evaluate your requirements and choose a platform that aligns with your business needs. Consider factors such as:
- Cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- Pricing models (pay-as-you-go, reserved instances)
- Security and compliance certifications
- Support and documentation
4. Design Your Migration Strategy
Based on your assessment and platform selection, develop a detailed migration strategy. This plan should outline:
- Migration approach (lift-and-shift, re-platforming, re-architecting)
- Migration scope (applications, data, infrastructure)
- Migration timeline (phased or full migration)
- Resource allocation (internal teams, external consultants)
- Testing and validation procedures
5. Execute and Monitor
With a well-defined strategy in place, begin the migration process. Execute the plan systematically, closely monitoring progress and addressing any challenges that arise. Continuous communication and collaboration between teams are essential for a successful transition.
6. Optimize and Refine
Post-migration, it’s important to continuously optimize and refine your cloud environment. Leverage cloud monitoring tools to track performance, identify bottlenecks, and make necessary adjustments to maximize efficiency and cost savings.
By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of cloud migration and achieve your desired outcomes. Remember, thorough planning, effective communication, and ongoing monitoring are key to a successful transition.
Selecting the Right Cloud Provider for Your Needs
With the rise of cloud computing, organizations of all sizes are moving their operations to the cloud. But with so many cloud providers available, choosing the right one for your needs can be a daunting task.
Here are some factors to consider when selecting a cloud provider:
Services Offered
Not all cloud providers offer the same services. Some providers specialize in specific areas, such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), or software as a service (SaaS). It’s important to choose a provider that offers the services you need.
Pricing
Cloud providers offer a variety of pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, subscription-based, and reserved instances. It’s important to compare prices and choose a provider that fits your budget.
Security
Security is a critical consideration when choosing a cloud provider. Look for providers that have strong security measures in place, such as encryption, access control, and compliance with industry standards.
Performance
The performance of your cloud infrastructure is important for your business operations. Choose a provider that has a proven track record of performance and reliability.
Support
You’ll need support if you have any issues with your cloud infrastructure. Look for a provider that offers 24/7 support and has a responsive support team.
Scalability
Your business needs will change over time. Choose a provider that offers scalable solutions so that you can adjust your cloud infrastructure as needed.
By considering these factors, you can select the right cloud provider for your needs and ensure a successful cloud migration.
Data Security in Cloud Migration: Best Practices
Moving to the cloud presents incredible opportunities for businesses, but it also introduces new security considerations. Ensuring your data remains protected during and after migration is critical. Here are key best practices for data security in cloud migration:
1. Comprehensive Security Assessment: Before migrating, conduct a thorough security assessment of your existing infrastructure and data. Identify vulnerabilities and potential risks to develop a robust mitigation strategy.
2. Choose Secure Cloud Providers: Select cloud providers with strong security certifications and proven track records. Look for features like data encryption at rest and in transit, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
3. Implement Strong Access Control: Establish granular access controls for your cloud environment. Only authorized personnel should have access to sensitive data. Leverage role-based access control (RBAC) to limit user permissions based on their job functions.
4. Encryption is Paramount: Encrypt data both at rest and in transit. Ensure your cloud provider offers robust encryption capabilities and that your own encryption protocols are aligned with industry best practices.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to detect and prevent unauthorized data transfers. DLP tools can monitor for suspicious activities and block attempts to move sensitive data outside of your cloud environment.
6. Regular Security Monitoring: Establish continuous security monitoring practices. Use cloud security tools to detect anomalies, suspicious activity, and potential breaches. Regularly review security logs and implement automated alerts for critical events.
7. Employee Training: Train employees on cloud security best practices and the importance of secure data handling. Emphasize the risks associated with phishing attacks, social engineering, and unauthorized access.
8. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Plan for disaster recovery and business continuity. Ensure that your cloud infrastructure is designed to withstand outages and that you have a process for restoring critical data in the event of a security breach.
By adhering to these best practices, you can significantly enhance data security throughout your cloud migration journey. Remember, a proactive and layered approach to security is essential for protecting your valuable data in the cloud environment.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Cloud Migration
Cloud migration offers numerous benefits, but cost optimization is a crucial aspect to consider. Efficiently managing cloud expenses can significantly impact your bottom line. Here are some effective strategies to optimize costs during and after your cloud migration:
Rightsizing Your Resources
One of the biggest cost drivers in the cloud is over-provisioning. Instead of paying for resources you don’t use, it’s essential to rightsize your infrastructure. This involves selecting the appropriate instance types, storage options, and scaling resources based on actual demand. Consider using auto-scaling capabilities to dynamically adjust resources according to workloads.
Leveraging Reserved Instances
Cloud providers offer reserved instances, which provide significant discounts for committing to a specific instance type and duration. If you have predictable workloads, reserving instances can significantly reduce costs compared to on-demand pricing.
Spot Instances and Preemptible VMs
For less critical workloads, explore spot instances or preemptible virtual machines. These instances offer deeply discounted pricing but are subject to termination with short notice. By strategically using these options, you can save significantly on costs for non-essential workloads.
Optimizing Storage
Cloud storage comes in various tiers with different pricing models. Select the appropriate storage class based on data access frequency and retention requirements. Utilize cold storage for infrequently accessed data and object storage for large datasets, minimizing storage costs.
Utilizing Cloud Monitoring Tools
Implement cloud monitoring tools to track resource usage and identify areas for optimization. These tools can help you identify underutilized resources, optimize resource allocation, and proactively address potential cost overruns.
Negotiating with Cloud Providers
Don’t hesitate to negotiate with your cloud provider for better pricing and discounts, especially for large deployments. Cloud providers are often willing to offer incentives to retain customers and attract new business.
Adopting a Cloud-Native Approach
Migrating to the cloud presents an opportunity to adopt cloud-native technologies such as containers, microservices, and serverless computing. These technologies offer greater efficiency and potentially lower costs compared to traditional infrastructure.
Regularly Reviewing and Optimizing
Cloud computing is a dynamic environment. It’s crucial to regularly review and optimize your cloud resources to ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment. Establish a process for periodic cost analysis and make necessary adjustments to your cloud deployment.
Managing Cloud Migration Risks and Challenges
Cloud migration offers numerous benefits, including increased agility, scalability, and cost optimization. However, it also presents potential risks and challenges that require careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies. This article delves into some of the key risks and challenges associated with cloud migration and outlines effective strategies to navigate them successfully.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns during cloud migration. Organizations must ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their sensitive data throughout the transition. It’s crucial to select a cloud provider with robust security measures, implement appropriate data encryption protocols, and adhere to relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Downtime and Service Disruptions
Migrating workloads to the cloud can potentially disrupt business operations if not planned and executed meticulously. It’s essential to minimize downtime by implementing a phased approach, conducting thorough testing, and leveraging tools for seamless data migration. Redundancy and disaster recovery plans are also crucial for mitigating service disruptions.
Cost Management
Cloud computing can be cost-effective, but it’s essential to manage costs effectively. Organizations need to understand the pricing models of their chosen cloud provider, optimize resource utilization, and implement cost monitoring tools. Regularly analyzing cloud spending and identifying areas for improvement can significantly reduce cloud migration costs.
Integration and Compatibility
Integrating cloud services with existing on-premises systems can pose challenges. Organizations must ensure compatibility between systems and data formats, identify potential integration points, and develop strategies for seamless data transfer and interoperability. It’s essential to involve relevant stakeholders from IT, business, and security teams.
Skill Gaps
Successful cloud migration requires a skilled workforce with expertise in cloud technologies, security practices, and migration processes. Organizations may need to invest in training programs, hire cloud specialists, or partner with cloud consulting firms to bridge skill gaps and build a competent cloud team.
Conclusion
Managing cloud migration risks and challenges requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing meticulous planning, robust security measures, effective cost management, seamless integration, and a skilled workforce. By addressing these key considerations, organizations can navigate the complexities of cloud migration and unlock the full potential of cloud computing.
Post-Migration Optimization and Management
After successfully migrating to the cloud, the journey doesn’t end. Post-migration optimization and management are crucial for maximizing the benefits and achieving long-term success with your cloud deployment.
Here’s a breakdown of key aspects to focus on:
- Performance Tuning: Analyze your cloud environment to identify bottlenecks and areas for performance improvement. Optimize resource allocation, caching mechanisms, and database configurations.
- Cost Optimization: Regularly review cloud spending to identify areas for cost reduction. Leverage cost management tools, right-size resources, and take advantage of cloud provider discounts.
- Security Enhancement: Implement robust security measures in your cloud environment, including access controls, encryption, and vulnerability scanning. Stay informed about evolving security threats and update your security practices accordingly.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Establish comprehensive monitoring systems to track key metrics like performance, availability, and resource utilization. Configure alerts to notify you of potential issues or anomalies.
- Continuous Improvement: Don’t settle for the initial migration configuration. Use data from monitoring and analysis to identify opportunities for further optimization and refinement of your cloud strategy.
By implementing these post-migration optimization and management practices, you’ll ensure your cloud environment remains efficient, secure, and cost-effective. This proactive approach helps you unlock the full potential of cloud computing and achieve your business objectives.
Cloud Migration Use Cases and Success Stories
Cloud migration has become a popular choice for businesses across various industries, offering numerous benefits like scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. But what exactly are the use cases for cloud migration, and what stories of success can we learn from? Let’s explore some compelling examples.
One prominent use case is modernizing legacy applications. Migrating aging applications to the cloud can significantly enhance performance, security, and agility. For instance, a large retail company migrated its decades-old point-of-sale system to the cloud, resulting in a faster, more reliable experience for customers and staff. The cloud platform allowed for seamless updates and scalability during peak seasons, eliminating previous performance bottlenecks.
Another compelling use case is disaster recovery and business continuity. By replicating critical data and applications on the cloud, businesses can ensure uninterrupted operations in case of unforeseen events such as natural disasters or cyberattacks. A financial services firm successfully implemented a cloud-based disaster recovery solution, enabling them to restore operations within hours after a major data center fire. This minimized downtime and financial losses.
Big data analytics is another area where cloud migration excels. The cloud’s vast processing power and storage capacity make it ideal for handling massive datasets. A pharmaceutical company leveraged the cloud to analyze patient data, identify potential drug targets, and accelerate drug discovery. This significantly reduced research time and costs, leading to faster development of life-saving treatments.
These are just a few examples of how cloud migration has transformed businesses across diverse sectors. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative use cases and success stories to emerge. By exploring these real-world examples, businesses can gain valuable insights into the potential benefits of cloud migration and tailor their strategies for optimal outcomes.
Future Trends in Cloud Migration Strategies
The cloud computing landscape is constantly evolving, bringing forth new technologies and approaches that are reshaping cloud migration strategies. As businesses continue to embrace the benefits of cloud adoption, understanding the latest trends is crucial for successful migration and ongoing success.
Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of cloud migration:
1. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is gaining traction as a powerful way to streamline cloud migration. This approach allows developers to focus on writing code without managing underlying infrastructure, making it more cost-effective and efficient. By eliminating the need for server provisioning and maintenance, serverless computing simplifies cloud migration and allows businesses to scale their applications on demand.
2. Cloud-Native Technologies
Cloud-native technologies, such as containers and microservices, are becoming essential for modern cloud migration strategies. These technologies enable businesses to build and deploy applications in a highly modular and scalable way, enhancing agility and flexibility. Embracing cloud-native principles allows organizations to leverage the full potential of the cloud, optimizing performance and resource utilization.
3. Edge Computing
Edge computing is emerging as a critical factor in cloud migration, particularly for applications that require low latency and high bandwidth. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces network congestion and improves response times. Incorporating edge computing into cloud migration strategies can enhance user experience and unlock new possibilities for real-time applications.
4. AI-Powered Migration Tools
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the way cloud migrations are conducted. AI-powered tools are being developed to automate various stages of the migration process, from assessment and planning to data migration and application testing. These tools streamline operations, reduce human error, and accelerate migration timelines, making the transition to the cloud more efficient and cost-effective.
5. Security and Compliance
As cloud environments become more complex, security and compliance remain top priorities. Future cloud migration strategies will focus on robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and threat detection. Organizations need to ensure their cloud deployments meet industry regulations and standards to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
By embracing these future trends, businesses can navigate the ever-evolving cloud landscape and achieve successful cloud migration outcomes. Implementing serverless computing, leveraging cloud-native technologies, incorporating edge computing, utilizing AI-powered tools, and prioritizing security and compliance are crucial elements of future-proof cloud migration strategies.

