In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, safeguarding your network has become paramount. With the increasing sophistication of hacking techniques, protecting sensitive data and maintaining business continuity requires a comprehensive approach to security. Building an impregnable fortress for your network demands a robust strategy that encompasses both preventative measures and proactive defenses.
This article will delve into the realm of effective network security solutions, exploring the essential components that underpin a secure and resilient infrastructure. We will examine cutting-edge technologies, best practices, and emerging trends that empower organizations to combat cyberattacks and safeguard their digital assets. From firewalls and intrusion detection systems to advanced threat intelligence and security awareness training, we will unravel the key elements that form the cornerstone of a secure network.
Understanding the Threat Landscape

In today’s digital age, where data is the lifeblood of businesses and individuals, securing our networks is paramount. However, building an impregnable fortress requires a thorough understanding of the ever-evolving threat landscape. This landscape is a dynamic ecosystem of malicious actors, sophisticated techniques, and emerging vulnerabilities, constantly posing threats to our digital assets.
One of the most significant threats is the rise of advanced persistent threats (APTs). These highly organized groups, often backed by nation-states, utilize sophisticated tools and techniques to infiltrate networks and steal sensitive information. Their attacks are often stealthy and long-lasting, making them difficult to detect and counter.
Another major concern is the proliferation of ransomware attacks. These malicious software programs encrypt critical data, holding it hostage until a ransom is paid. The impact of ransomware can be devastating, disrupting operations and causing significant financial losses.
Furthermore, the growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has introduced new vulnerabilities. These interconnected devices often lack adequate security features, making them easy targets for attackers. Exploiting vulnerabilities in IoT devices can provide attackers with access to sensitive data and control over critical infrastructure.
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging and existing ones becoming more sophisticated. Understanding the nature of these threats, their tactics, and their motives is crucial for developing effective security solutions. By staying informed and adapting our defenses, we can build robust network security that can withstand the ever-growing onslaught of cyberattacks.
Essential Components of Network Security
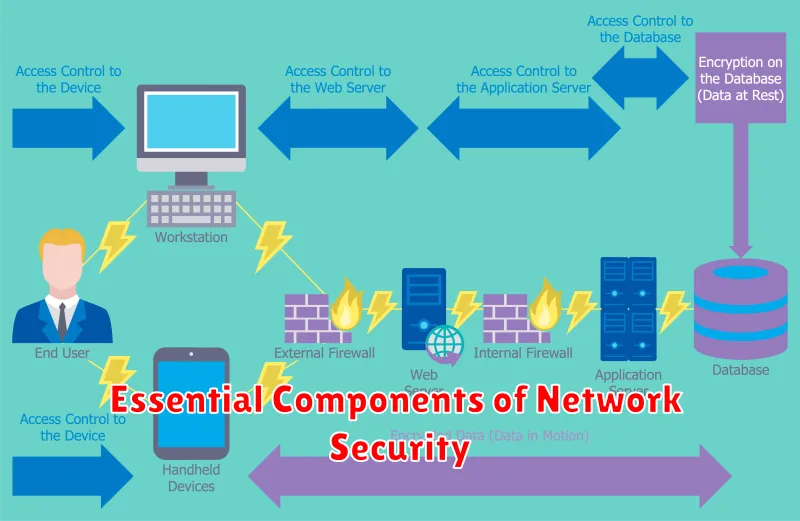
Building a robust network security posture requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing several essential components that work together to create a comprehensive defense system. These components act as the building blocks of an impregnable fortress, safeguarding your network and its valuable data from threats.
Firewalls are the first line of defense, acting as digital gatekeepers that control incoming and outgoing network traffic. They examine each packet of data, allowing only authorized traffic to pass through while blocking malicious attempts. Think of them as the fortified walls of your castle, preventing intruders from entering.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) constantly monitor network activity for suspicious patterns and potential threats. They can detect intrusions in real time and take appropriate actions, such as alerting administrators or blocking malicious traffic. These are the vigilant guards within your castle, constantly scanning for signs of danger.
Anti-malware software plays a crucial role in protecting against malicious programs that can harm your network and steal data. It identifies and removes viruses, worms, Trojans, and other threats before they can cause damage. This safeguards your digital assets from internal threats.
Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are critical for securing user accounts. By using complex passwords and adding an extra layer of authentication, you make it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access sensitive data. This is like having a complex lock and key system on your castle’s doors.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses in your network security. By conducting these assessments, you can proactively identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary fixes, ensuring a secure network environment. This is akin to regularly inspecting your castle walls and making repairs as needed.
User education and awareness play a critical role in network security. By educating users on safe practices, such as avoiding phishing scams and recognizing malicious emails, you can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to breaches. This involves training your castle’s inhabitants on how to spot and avoid potential threats.
Implementing these essential components of network security, you can build a strong defense against cyber threats and ensure the safety of your network and its valuable data. Remember, a robust security posture is an ongoing process, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats. By staying informed and implementing best practices, you can confidently navigate the digital landscape and protect your network from attack.
Firewall: Your First Line of Defense
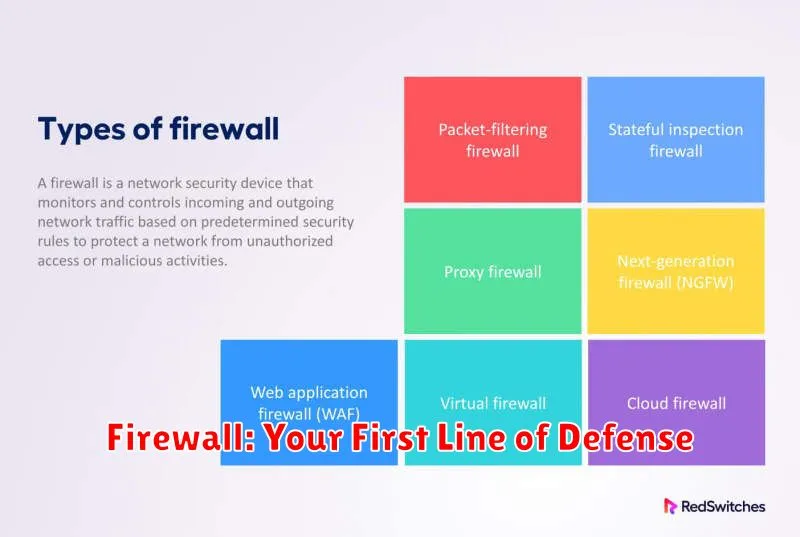
In the digital age, safeguarding your network from threats is paramount. A firewall stands as your first line of defense, acting as a vigilant guardian against unauthorized access and malicious attacks. Think of it as a robust gatekeeper, meticulously inspecting all incoming and outgoing traffic, allowing only legitimate connections to pass through.
Firewalls function by implementing a set of pre-defined rules, carefully crafted to identify and block suspicious activity. These rules can be as simple as restricting access from specific IP addresses or as sophisticated as analyzing network protocols and content to detect malware. By meticulously scrutinizing network traffic, firewalls prevent unauthorized access, protect against data breaches, and safeguard your network from various cyber threats.
Firewalls are essential components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. They form the foundation upon which you can build additional layers of protection, such as intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and user authentication measures. A strong firewall, combined with other security measures, creates a robust and multi-faceted defense system, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks and safeguarding your valuable data.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
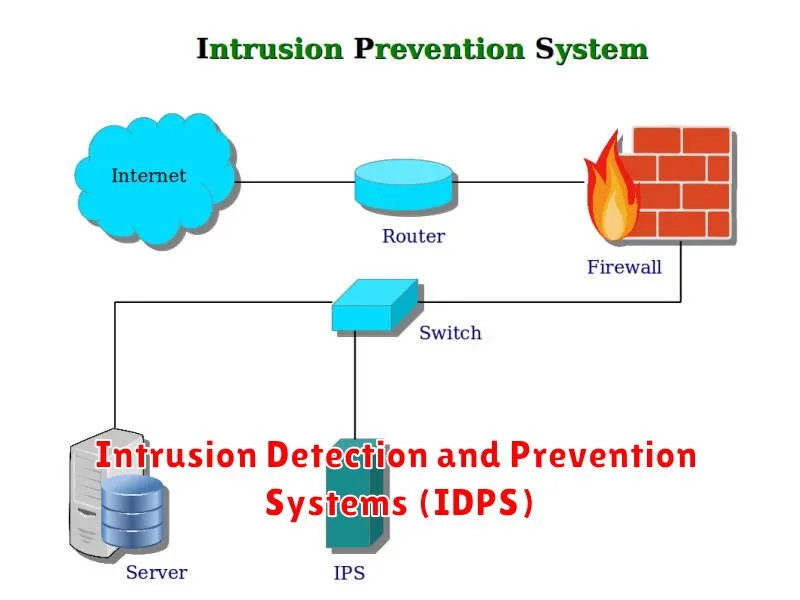
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining network integrity is paramount. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) play a crucial role in bolstering network security by detecting and mitigating malicious activities. These systems act as vigilant guardians, constantly monitoring network traffic for suspicious patterns and implementing appropriate countermeasures.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) primarily focus on identifying potential threats. They analyze network traffic for known attack signatures and anomalies, generating alerts when suspicious activity is detected. While IDS are passive in nature, they provide invaluable insights into the nature and scope of attacks, enabling timely responses and incident investigation.
On the other hand, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) take a more proactive approach. They not only detect threats but also actively block or prevent malicious traffic from reaching target systems. IPS employ various mechanisms, such as packet filtering, deep packet inspection, and traffic shaping, to mitigate potential attacks before they can cause significant damage.
The effectiveness of IDPS hinges on several factors, including:
- Signature Database: Maintaining a comprehensive and up-to-date signature database is crucial for identifying known attack patterns.
- Anomaly Detection: Detecting unusual or unexpected behavior in network traffic is essential for identifying zero-day attacks and novel threats.
- Response Mechanisms: Effective response mechanisms, such as blocking malicious traffic, generating alerts, or triggering incident response procedures, are essential for mitigating threats.
IDPS are integral components of a robust cybersecurity strategy, providing an essential layer of protection against a wide range of threats. By combining the power of detection and prevention, these systems empower organizations to proactively defend their networks, safeguarding critical data and ensuring business continuity.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for Secure Connections
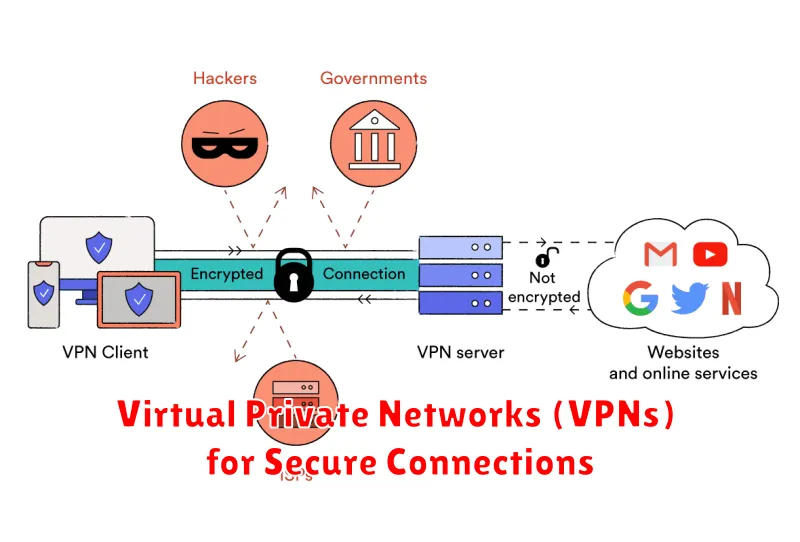
In the digital age, safeguarding our online activities is paramount. While the internet provides a vast array of opportunities, it also presents significant security risks. One potent tool for bolstering network security is the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). VPNs act as a secure tunnel, encrypting your internet traffic and masking your IP address, thereby safeguarding your online activities from prying eyes.
VPNs are particularly beneficial when using public Wi-Fi networks, as these networks are inherently less secure. When you connect to a public Wi-Fi network without a VPN, your data is transmitted unencrypted, making it vulnerable to interception by malicious actors. By utilizing a VPN, you create a secure connection, ensuring your data remains private and confidential.
Furthermore, VPNs can be instrumental in accessing geo-restricted content. Many websites and streaming services restrict access based on your geographical location. By connecting to a VPN server in a different location, you can effectively bypass these restrictions and enjoy content that would otherwise be unavailable.
Choosing the right VPN is crucial. Consider factors such as security features, server network coverage, and privacy policies. Reputable VPN providers offer robust encryption protocols, a strict no-logs policy, and a wide selection of server locations. By investing in a reliable VPN, you can enhance your online security and privacy, creating a more impregnable fortress for your digital life.
Securing Your Wireless Network

In today’s interconnected world, securing your wireless network is more crucial than ever. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, safeguarding your data and privacy requires a proactive approach. An impregnable fortress starts with a solid foundation – a secure wireless network.
Here are some key steps to fortify your wireless network:
- Strong Password Protection: Utilize a complex password for your router and avoid using default credentials. A robust password with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols is essential to deter unauthorized access.
- Enable WPA2/WPA3 Encryption: Ensure your router supports and utilizes the latest encryption protocols such as WPA2 or WPA3. These protocols scramble data transmissions, making it difficult for hackers to intercept and decipher your information.
- Change Default SSID: The default network name (SSID) is often easily identifiable, making it a target for attackers. Modify it to a unique and less obvious name to enhance security.
- Disable WPS: Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) can be a security vulnerability. Disabling it helps prevent attackers from exploiting WPS loopholes to gain access to your network.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Keep your router firmware up-to-date to benefit from security patches and vulnerability fixes. Manufacturers release updates to address emerging threats and enhance security.
- Use a Firewall: Implement a firewall on your router or network devices to act as a barrier between your network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
- Limit Network Access: Restrict network access to authorized devices by enabling MAC address filtering or using guest networks. This prevents unauthorized devices from connecting to your network.
- Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic, providing an extra layer of protection when using public Wi-Fi hotspots or accessing sensitive data online.
By implementing these measures, you can significantly enhance the security of your wireless network, creating a digital fortress that protects your data and privacy. Remember, a secure wireless network is the foundation of a safe and reliable online experience.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies

Data loss prevention (DLP) is a critical aspect of network security, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Implementing robust DLP strategies is essential to protect your organization’s valuable assets and ensure regulatory compliance.
Here are some effective DLP strategies to consider:
- Data Classification and Labeling: Categorize data based on sensitivity levels (e.g., confidential, internal, public) and assign appropriate labels. This enables you to implement granular security controls.
- Endpoint Security: Secure endpoints (laptops, mobile devices) by implementing encryption, access control, and data loss prevention software. This prevents unauthorized access and data leakage.
- Network Security: Use firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and network segmentation to monitor and control network traffic, blocking suspicious activities and preventing data exfiltration.
- Data Loss Prevention Software: Implement DLP software to monitor data flow, detect suspicious activities, and prevent unauthorized data transfers. It can scan emails, files, and web traffic for sensitive information.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about data security policies, best practices, and potential threats. Regular training helps them understand the importance of data protection and avoid unintentional data leaks.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical data and ensure robust disaster recovery plans are in place. This minimizes data loss in case of system failures, cyberattacks, or accidental deletions.
- Incident Response: Establish clear incident response protocols for handling data breaches. This involves timely detection, containment, investigation, and remediation to minimize damage.
- Regular Reviews and Updates: Regularly review and update your DLP strategies to adapt to evolving threats and ensure effectiveness. Keep up-to-date with industry best practices and emerging technologies.
By implementing these comprehensive DLP strategies, you can build an impregnable fortress, safeguarding your valuable data from malicious actors and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your organization’s information.
Endpoint Security: Protecting Devices at the Edge

In today’s increasingly mobile and interconnected world, securing the edge of your network is paramount. Endpoint security plays a crucial role in this endeavor, protecting individual devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets from cyber threats. These devices are often the first line of defense against malicious actors, making their protection essential.
Think of endpoint security as a personal bodyguard for each device on your network. It encompasses various security measures to safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access, including:
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: These tools detect and remove known threats like viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Firewall Protection: Firewalls act as a barrier, blocking unauthorized access to your device’s network connections.
- Data Encryption: Encryption safeguards sensitive information by transforming it into an unreadable format, protecting it even if the device falls into the wrong hands.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert you to potential threats.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions go beyond traditional endpoint security by providing advanced threat detection, investigation, and response capabilities.
By implementing robust endpoint security measures, you can create a more secure network perimeter, minimize the risk of data breaches, and protect your organization from costly downtime. Investing in comprehensive endpoint security solutions is a critical step in building an impregnable fortress against cyber threats.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
In the realm of cybersecurity, a robust defense strategy is essential for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of critical systems. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) plays a pivotal role in this endeavor, acting as the central nervous system for monitoring, analyzing, and responding to security threats.
At its core, SIEM consolidates security data from diverse sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, and logs from various applications. This aggregation of information provides a comprehensive view of network activity, enabling security professionals to detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and react swiftly to incidents.
One of the key strengths of SIEM is its ability to correlate events across different systems. By analyzing patterns and relationships among various security events, SIEM can detect complex attacks that might otherwise go unnoticed. This real-time threat detection capability allows organizations to proactively mitigate risks and respond effectively to evolving cybersecurity landscapes.
Furthermore, SIEM empowers organizations with robust incident response capabilities. By providing a centralized platform for managing security events, SIEM facilitates rapid investigation, analysis, and remediation of security incidents. This streamlined approach minimizes downtime, reduces potential damage, and helps restore systems to their normal operating state quickly.
The adoption of SIEM is a critical step towards building an impregnable fortress for your organization’s network security. By leveraging its powerful capabilities, businesses can enhance threat detection, accelerate incident response, and gain valuable insights into their security posture.
Regular Security Audits and Updates

In the digital age, cybersecurity is paramount. Building an impregnable fortress for your network requires a multi-faceted approach, and one of the most crucial elements is regular security audits and updates. These practices are like the routine maintenance of a physical fortress, ensuring its strength and resilience against potential threats.
Security audits are comprehensive assessments of your network’s security posture. They involve analyzing your systems, configurations, and policies to identify vulnerabilities and potential weaknesses. These audits can be conducted internally or by external experts, offering a fresh perspective and a deeper understanding of your network’s security risks.
Regular updates are equally essential. Software and firmware often contain vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. By updating your systems regularly, you patch these vulnerabilities, reducing the likelihood of a successful attack. This includes updating operating systems, applications, and even firmware on network devices.
The frequency of security audits and updates should be tailored to your specific needs and risk profile. However, a general guideline is to conduct audits at least annually and to implement updates as soon as they are available.
By prioritizing regular security audits and updates, you create a proactive and preventative security strategy. This approach helps you stay ahead of emerging threats and ensures that your network remains protected against evolving cyberattacks. Remember, a robust cybersecurity strategy is an ongoing process, and consistent vigilance is key to maintaining a truly impregnable digital fortress.
Employee Training and Awareness

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, employee training and awareness are crucial components of a comprehensive network security strategy. By empowering employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and mitigate potential threats, organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses against cyberattacks.
Effective employee training programs should cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Understanding how attackers manipulate individuals into compromising systems through deceptive emails, messages, or calls.
- Password Security: Emphasizing the importance of strong passwords, avoiding reuse, and implementing multi-factor authentication.
- Data Security Best Practices: Educating employees on proper handling of sensitive data, including access control, encryption, and secure storage.
- Malware Awareness: Familiarizing employees with the types of malware, how they spread, and how to prevent infection.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity: Encouraging employees to report any unusual or suspicious activity to security personnel immediately.
Beyond theoretical knowledge, practical exercises and simulations are essential to solidify understanding and build skills. Role-playing scenarios, phishing tests, and interactive training modules can help employees apply their learnings in real-world situations.
Regular training and awareness campaigns are crucial to maintain vigilance. By continuously educating employees about emerging threats, best practices, and latest security measures, organizations can keep their defenses strong and prevent complacency.

